
Java EE is
a Java platform
(Java EE Components in picture) [
JavaEE Platform,
Technologies,
all
APIs
] designed for the
mainframe-scale
computing typical of large enterprises.
Sun Microsystems (together with industry partners such as IBM) designed J2EE to simplify
application development in a thin client tiered environment.
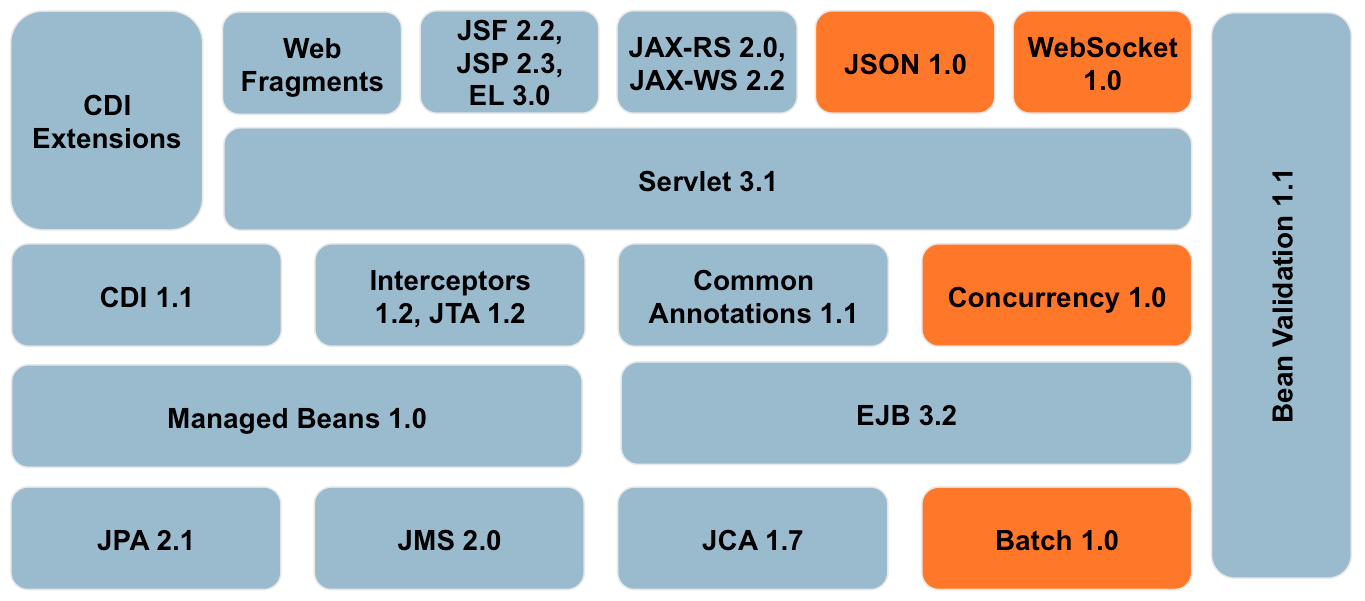
J2EE simplifies application
development and decreases the need for programming and programmer training by creating
standardized, reusable modular components and by enabling the tier to handle many aspects of
programming automatically. [1]
Java EE Platform includes Java
Standard Edition plus most of the other Java technologies including Java Specialized Topics,
Activation,
JMS (Java Messaging Service), EJB and more others .
Most of the APIs are very component-oriented and are intended to provide pluggable interfaces for business components to form robust, distributed internet applications.
About Java Servlets, JSPs, JSFs, Portlets and EJBs
A servlet (it is used for creating Java web-apps) is a Java programming language class used to extend the capabilities of servers that host applications accessed via a request-response programming model.
Although servlets can respond to any type of request, they are commonly used to extend the applications hosted by Web servers. For such applications, Java Servlet technology defines HTTP-specific servlet classes. JSP is a technology, (see also jsp+servlet) not a language. It allows Web page authors to put dynamic data into a Web document with Java statements embedded in special HTML tags. The embedded Java statements will be executed by the JSP enabled Web server, not by the Web browser.
On the Web, a portlet (see more: JSR 286, portlet types, Open Source Portals in Java) is a component of a portal. Web site that provides access to some specific information source or application, such as news updates, technical support, or an e-mail program among many other possibilities. Portals aggregate different content into a single interface; portlets connect the user to specific content within that interface. Most portals offer a selection of portlets that the user can select for a customized interface. Portals connect to portlets through portlet APIs (application programming interfaces).
JSF (1, EL2, 3) is a component based MVC framework which is built on top of the Servlet API and provides components in flavor of taglibs which can be used in JSP or any other Java based view technology such as Facelets.
Enterprise
JavaBeans (EJBs)
are used for developing scalable, distributed, server-side components
and typically encapsulate the business logic of the application.
An EJB (see also Spring and EJB Framework,
Understanding EJB,
setup EJB,
EJB and JPA components
), is a managed, server-side component architecture for modular construction of
enterprise applications.
Java web services (Building Web
Services with JAX-WS) provide a standard means of interoperating between software
applications running on a variety of platforms and frameworks. Whereas
RESTful web
services (examples: JAX-RS, Spring REST)
are built to work best on the web on an architectural style REST.
Books more about the Java EE components:
Java for the WEB,
Head first servlets & JSP,
Portlets for Portals,
Ejb 3 in Action,
Pro EJB 3: Java Persistence API,
Pro JPA 2,
JSTL in Action,
Java Server Faces In Action,
Enterprise Practices,
Pro JSF and Ajax: ,
Portlets in Action,
Liferay in Action
Java EE Tutorials
Other Tools: Java Toolkit • API's • Programmer's Corner • WebDev. Tools • Database Tools • Modeling & Design • Multimedia (AI Tools) • Maths and Science
Application Servers ⇧
An application server is a server program that handles all application operations between users and an organization's backend business applications or databases. Application servers are typically used for complex transaction-based applications. To support high-end needs, an application server has to have built-in redundancy, monitors for high-availability, high-performance distributed application services and support for complex database access. See the following application servers and other Web Servers in Java, Network Servers in Java:
|
|
Comparision of application servers: List of application servers, J2EE Performance, Tomcat alternatives, App.Servers, Diff. between a Web Server and an Application Server, Web Server vs Application Server, Comparison of web server software
Suggested Reading:
J2EE
Containers
• Web
Container
• WebLogic
• Load Balancing
• L.B. Architectures
• L.B
and failover
• Clustering and L.B
• JBoss clustering
• CORBA
Technology
• with Java
• 2
• CORBA
Technology
• JBoss at Work
•
CORBA and
Applets/SecurityManager
References
- 1. Java EE at a Glance
- 2. Java Platform, Enterprise Edition
- 3. Make the Future Java
- 4. Java EE 7 Launch Webinar Technical Breakouts
- 5. Java EE 7 Technologies