
Server (different server types) is
primarily a program that runs on a machine, providing a particular and specific service to
other machines connected to the machine on which it is found. Generally speaking, a server
is a machine with a specific set of programs that offer different types of service, which
other machines (then called clients) request to do certain tasks. For example, a
file server is a
machine which keeps files, and allows clients to upload and download them from it. A web server is a machine that hosts web sites and allows Internet
users (clients) to access these web sites.[1]
In other words, software servers (Software vs. Hardware: Understanding the Difference ) are programs that run on computer hardware and provide services to other computers (clients) over a network. They handle requests, manage resources, and facilitate communication between clients and the resources they need. Examples of software servers are: a. Programs, not physical machines b. Service providers (Apache, Nginx, etc.) They listens requests, and process them and responds accordingly. Their functionalities are: resource sharing, centralized management, and network communication. Here are some common types of servers:
A cloud server is a powerful physical or virtual infrastructure, hosted remotely by
a
cloud service provider, that delivers applications, processes information or provides
data storage.
A cloud server is
a virtualized server that runs in the cloud on infrastructure owned by a
cloud service provider.
Traditionally, organizations had to purchase and maintain their own
physical servers.
They used the servers to run and host applications and compute workloads
required for data processing and analytics. The servers were located on-site or in nearby
data centers. Today, your organization can spin up virtual cloud servers anywhere in the
world. These virtual spaces run on physical servers that are purchased and maintained by
third-party cloud providers. The virtual server replica, or cloud server, gives the same
performance, configuration options, and usability as a physical server machine. You can
access unlimited cloud servers in hundreds of different configuration types. With this kind
of power, you can run and host all types of applications and workloads in the cloud.
[6]
Client Server Networks
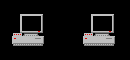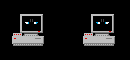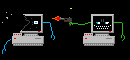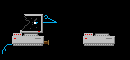
The term client-server model refers to a popular model for computer networking that utilizes client and server devices each designed for specific purposes. The client-server model can be used on the Internet as well as local area networks (LANs), see examples of client-server systems.
Client and Server Devices
Client devices are typically PCs with network software
applications installed that request and receive information over the network. Mobile devices
as well as desktop computers can both function as clients.
A server device typically stores files and databases
including more complex applications like Web sites. Server devices often feature
higher-powered central processors, more memory, and larger disk drives than clients.
Client-Server Applications
The client-server model distinguishes between applications as
well as devices. Network clients make requests to a server by sending messages, and servers
respond to their clients by acting on each request and returning results. One server
generally supports numerous clients, and multiple servers can be networked together in a
pool to handle the increased processing load as the number of clients grows.
Some of the most popular applications on the Internet follow the
client-server model including
Web browsers,
email,
FTP clients,
Web services,
Web servers
and DNS.
Each of these clients features a user interface (either graphic- or text-based) and a client
application that allows the user to connect to servers. In the case of email and FTP, users
enter a computer name (or sometimes an IP address) into the interface to set up connections to the server.
Client-Server vs Peer-to-Peer and Other Models
The client-server model was originally developed to allow more users to share access to database applications. Compared to the mainframe
approach, client-server offers improved scalability because connections can be made as
needed rather than being fixed. The client-server model also supports modular
applications that can make the job of creating software easier. In so-called
"two-tier" and "three-tier" types of client-server systems, software
applications are separated into modular pieces, and each piece is installed on clients or
servers specialized for that subsystem.
[1]
A network server is a computer designed to process requests and deliver data to other (client) computers over a local network or the Internet. Network servers typically are configured with additional processing, memory and storage capacity to handle the load of servicing clients. Any computer can be a "network server". What separates a server from a workstation is not the hardware, but rather the function performed by the computer. In general, a workstation is any computer used by an individual person to perform his or her job duties, while a network server is any computer that provides users with access to shared software or hardware resources.
Networking in JAVA
The Java networking is designed from the ground up to support concurrent programming, and java networking.
Peer-to-Peer ⇧
Client-server is just one approach to managing network
applications The primary alternative,
peer-to-peer
networking, models all devices as having equivalent capability rather than
specialized client or server roles.
Compared to client-server, peer to peer networks
offer some advantages such as more flexibility in growing the system to handle large
number of clients. Client-server networks generally offer
advantages in keeping data secure.
P2P networks are useful for applications that require decentralized collaboration,
resource
sharing, or secure and transparent transactions. However, P2P networks may not be suitable
for applications that require centralized control, high levels of security, or ones in which
legal issues are a concern.
Explore peer-to-peer networks, how they work, their creation when their best uses are, and
some examples for you to see real-life use cases.
Web Servers - See related web components ⇧
A Web server is a program that, using the client/server model and the World Wide Web's HTTP, serves the files that form Web pages to Web users. Leading Web servers are Apache , the most widely-installed Web server, and Microsoft's Internet Information Server. Other Web servers include Novell's Web Server for users of its NetWare operating system and IBM's family of Lotus Domino servers, primarily for IBM's OS/390 and AS/400 customers. Web servers often come as part of a larger package of Internet- and intranet-related programs for serving e-mail, downloading requests for FTP files, and building and publishing Web pages. Considerations in choosing a Web server include how well it works with the operating system and other servers, its ability to handle server-side programming, security characteristics, and publishing, search engine, and site building tools that may come with it.[2]. Here are some examples:
Apache
Apache is generally
recognized as the world's most popular Web server (HTTP server). Originally designed for
Unix servers, the Apache Web server has been ported to Windows and other network operating systems (NOS). The
name "Apache" derives from the word "patchy" that the Apache developers
used to describe early versions of their software.
The Apache Web server provides a full range of Web server features, including CGI, SSL,
and virtual
domains. Apache also supports plug-in modules for extensibility. Apache is reliable,
free, and relatively easy to configure (About).
IIS
IIS is Microsoft's business-class Web server (About). Some corporations choose IIS as their Web server because it is supported by a commercial organization. Some have criticized IIS in the past, though, for its alleged security weaknesses. IIS has improved over the years, supports many Web standards including SSL, and integrates well with other Microsoft Web technologies such as FrontPage. Web developers can use Microsoft's Active Server Page (ASP)technology, which means that applications - including ActiveX controls - can be imbedded in Web pages that modify the content sent back to users. Developers can also write programs that filter requests and get the correct Web pages for different users by using Microsoft's Internet Server Application Program Interface (ISAPI) interface. An admininstrator can manage IIS through a graphical console, the Internet Services Manager.
Nginx
Nginx is a web server that can also be used as a reverse proxy, load balancer, mail proxy and HTTP cache. Nginx is known for flexibility and high performance with low resource utilizatio. Documentation explaining how to configure NGINX and F5 NGINX Plus as a web server, reverse proxy, or application gateway.
More about: • Web Server Configuration • Application Servers • Deployment