
Theoretical Computer Science
(TCS) is mathematical and abstract in
spirit, but it derives its motivation from practical and everyday computation.
Its aim is to understand the nature of computation and,
as a consequence of this understanding,
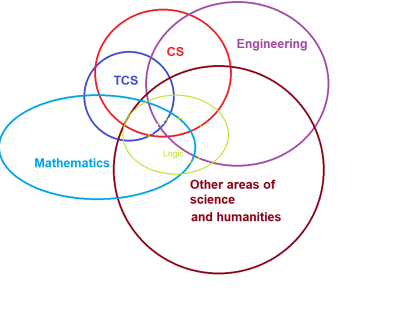 provide more efficient methodologies [1].
We can study theoretical aspects as below groups, whereas for their usage and applications see: Computational Science and Tools used for Computation.
Also,
STEM
industry
(short for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math), with a heavy emphasis on computer science at the
top. Four out of the top five spots went to Data Scientist, DevOps Engineering, Data Engineer, and
Analytics Manager.
provide more efficient methodologies [1].
We can study theoretical aspects as below groups, whereas for their usage and applications see: Computational Science and Tools used for Computation.
Also,
STEM
industry
(short for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math), with a heavy emphasis on computer science at the
top. Four out of the top five spots went to Data Scientist, DevOps Engineering, Data Engineer, and
Analytics Manager.
- Programming language theory
- Information and coding theory
- Formal methods
- Theory of computation (Number and Graph Theory, Cryptography, etc.)
- Algorithms and data structures (Computational Geo., Algorithm Analysis)
Programming Language Theory
Programming language theory (PLT) is a branch of computer science that deals with the design, implementation, analysis, characterization, and classification of formal languages known as programming languages. Programming language theory is closely related to other fields including linguistics, mathematics, and software engineering.
Information and Coding Theory
Both - related
aspects of the problem of how to transmit information efficiently and accurately. Information theory is
related
to the quantification of information, firstly used to find fundamental limits on signal processing
operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and communicating data. Coding theory is the study of
the
properties of codes. Codes are used for data compression, cryptography, error detection and
correction, and more recently also for network coding. Codes are studied for the purpose of
designing efficient and reliable data transmission methods.
See also: Selected Topic, International Journal, Book, Information Theory, Notes
Formal Methods
Formal methods are a particular kind of mathematically based technique for the specs., development and verification of software/ hardware systems.
Theory of Computation
The study of computation aims at providing an insight into the characteristics of computations. Such an insight can be used for predicting the complexity of desired computations, for choosing the approaches they should take, and for developing tools that facilitate their design [2].
Algorithms and Data Structures
An algorithm (pronounced AL-go-rith-um) is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. The word derives from the name of the mathematician, Mohammed ibn-Musa Al-Xorazmiy, born in Khiva (now in Uzbek) who was a scholar in the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, lived from about 780 to 850. Al-Khwarizmi's work is the likely source for the word algebra as well. A computer program can be viewed as an elaborate algorithm. In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm usually means a small procedure that solves a recurrent problem. In programming, the term data structure refers to a scheme for organizing related pieces of information. [3] A nice lecture by Brad Miller and David Ranum, Luther College Problem Solving with Algorithms and Data Struvtures. Also simple explanation about Data Structure - Sorting Techniques, Big O Complexities, Data Structure - Sorting Techniques
Practical examples: • Algorithms, • geeksforgeeks, Videos • algoritmy.net, • Transport Problem • Heuristic Search • Heaps • Alg 4th Edt.
Computational Geometry
Computational geometry is a branch of computer science devoted to the study of algorithms which can be stated in terms of geometry.
See also: Algorithms and Applications, CG Algorithms Library, Book, Computational Geometry course
Analysis of Algorithms
Analysis of Algorithms determines the amount of resources (such as time and storage) needed to execute them. Most algorithms are designed to work with inputs of arbitrary length.
See also: Research Focus, Design & Analysis, References, Books, with Java, with C++, with C#, Red Black Tree
Data Structures
Data Structures are a group of data elements grouped under one name. These elements can have different types and lengths.
See also: List of structures, Lecture, Java implementation, C++ implementation, cplusplus, Python
Algorithms
Algorithms are procedures or formulas for solving problems. The word derives from mathematician Mohammed ibn-Musa Al-Khwarizmi.
See also: Algorithms in Java, Distributed, Online Book, Java Collections, Lecture, Algorithms and DS in Java
Algorithms and Data Structures: Dijkstra’s Algo, What are Data Structures?, Research, Vimp, Handbook